<- Flow Torch 400s
Flow Torch 800s ->
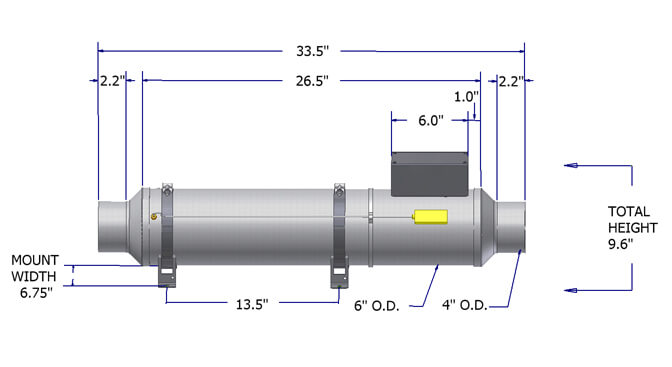
The Flow Torch™ 600 is an open coil air heater designed for high flow rates at low pressure drop due to its efficient design with minimal flow restrictions. The robust construction of this 6” diameter stainless steel heater offers reliable long-life performance and reduced operational cost.
The Flow Torch™ 600 incorporates a spiral wound element of the highest grade material, providing quick heat up and cool down cycles with maximum heat transfer.
The Flow Torch™ 600 is capable of operating with airflow of 1100 SCFM and a maximum operating pressure of 3 PSIG*. Maximum output temperature is 482 °C (900 °F).
All Flow Torch Heaters are UL recognized components under UL file number E365755.
Regenerative Blowers available with complete systems.
* Note: minor leakage through stranded leads
| MAX WATT | MAX INLET | MAX EXHAUST | MIN SCFM | MAX SCFM | PSIG* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60000 W | 250 °F | 900 °F | 38 | 1100 | 3 |
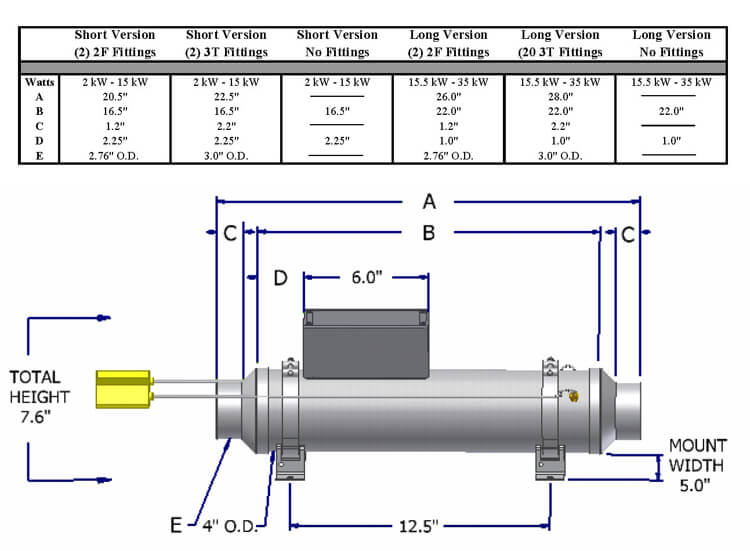
Mounting.= Horizontal / Vertical
Heater Body = Stainless Steel
Inlet Fittings = Stainless Steel
Exhaust Fittings = Stainless Steel
Applications include:
- Hot Air Curtains
- Laminating
- Plastic Curing
- Air Drying
- Web Drying
- Metallization
- Baking
- Textile Applications
- Exhaust Gas Heating
- Chemical Processing
- Ink Drying
- Hopper Drying
- Dehumidification
- Paint Baking/Drying
- Sterilization
Control Panels are also available to provide precise temperature regulation.
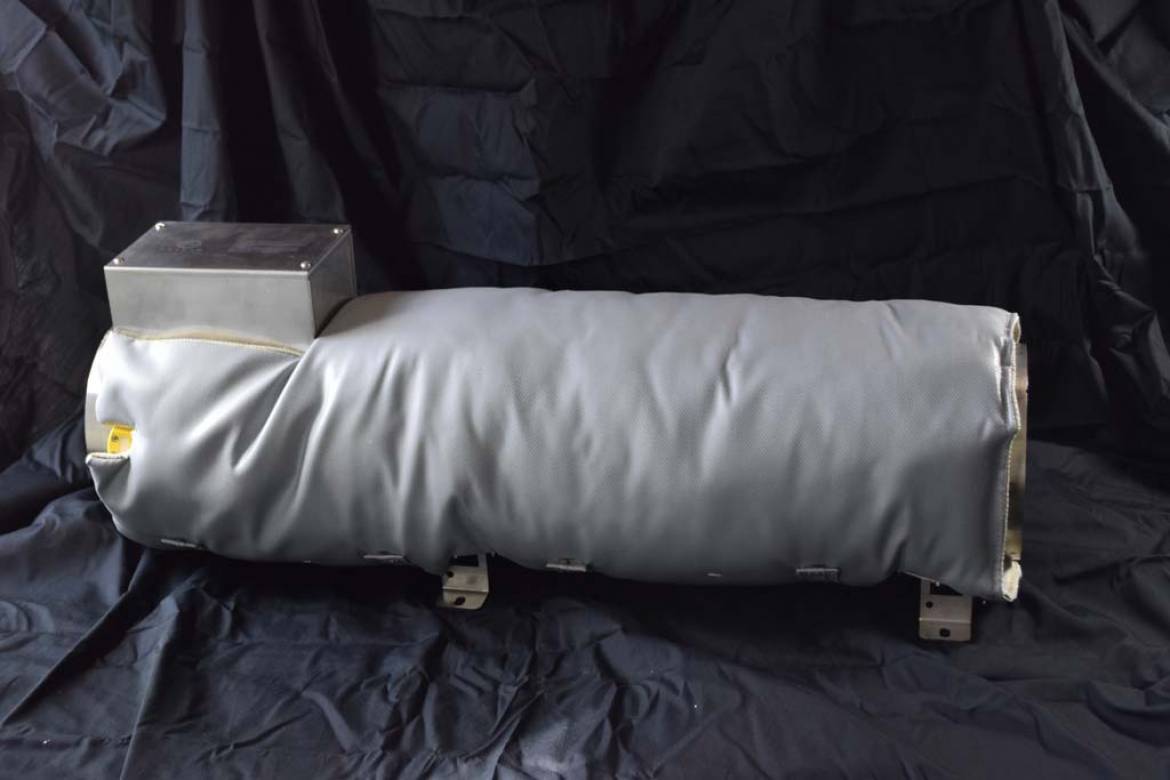
Insulation Jacket

Improve Safety
Using an insulation blanket reduces the burn hazard of any Flow torch installation quickly and easily. For example, if a Flow Torch is producing 500°F exhaust temperatures, it would be safe to estimate the outer surface of the Flow Torch heater is 500°F at the exhaust end. With the insulation blanket installed, the maximum outside surface temperature of the insulation blanket is only 110°F, completely removing the chance of an accidental burn hazard. The table below gives a more thorough listing of insulation temperatures expected for a range of heater operating temperatures.
Tutco–Farnam is pleased to announce that we are offering of high-temperature insulation blankets. These insulation blankets are specifically tailored for use with the Tutco–Farnam Flow Torch® family of heaters. A specific insulation blanket is available for Flow Torch® with an outside diameter of 4in, 6in, & 8in.
Simple Installation
The insulation blankets are easily installed in seconds. The insulation blanket is simply wrapped around the outside diameter of the Flow Torch®, and held in place by cinching up the integral straps and D-rings.
High-Temperature Materials
These are high-quality insulation blankets that use high-temperature materials throughout. The inside face that contacts the Flow Torch surface consists of a high-temperature textile called Vextra, which is rated for continuous use at up to 1000°F. The interior of the 1” thick blanket is filled with a needled non-woven fiberglass mat rated for continuous temperatures of 1000°F (excursions up to 1200°F ) as well. The outside surface of the blanket is fiberglass cloth coated with a specially formulated flame-retardant silicone rubber. This coating gives the blanket improved resistance to abrasion, tears, and punctures, yet it is very soft and flexible. All the materials used in these blankets have good chemical resistance and are non-combustible or flame retardant.
Product Fittings
|
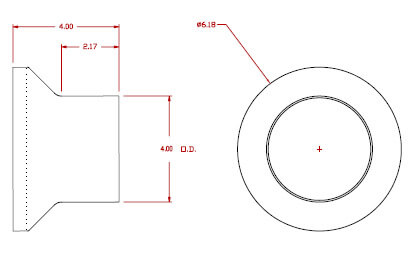
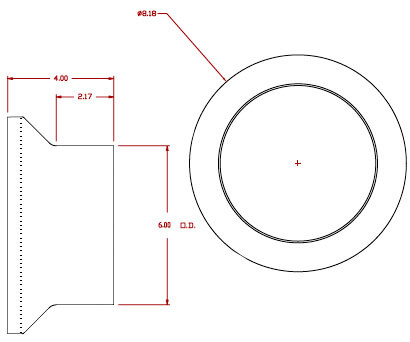
Exhaust Fitting 6″ Diameter Tube |
Exhaust Fitting 4″ Diameter Tube |
|
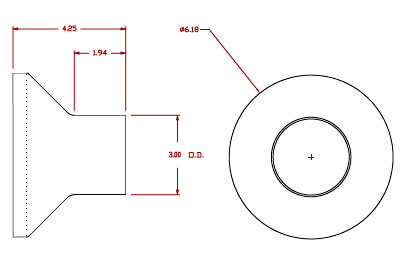
Exhaust Fitting 3″ Diameter Tube |
Exhaust Fitting 11″ Flanged Fitting |
 Inlet Fitting 3″ Diameter Tube Inlet Fitting 3″ Diameter Tube |
Inlet Fitting 11″ Flanged Fitting |
|
Inlet Fitting 6″ Diameter Tube |
Inlet Fitting 4″ Diameter Tube |
Pressure drop Chart (without fittings)

Pressure drop chart (with fittings)